In today's post, we explore the function of a skills matrix—a powerful tool that visually maps employee skills and competencies. We'll discuss how it helps identify skill gaps, guide training efforts, and support effective decision-making within your organisation.
What is a Skills Matrix?
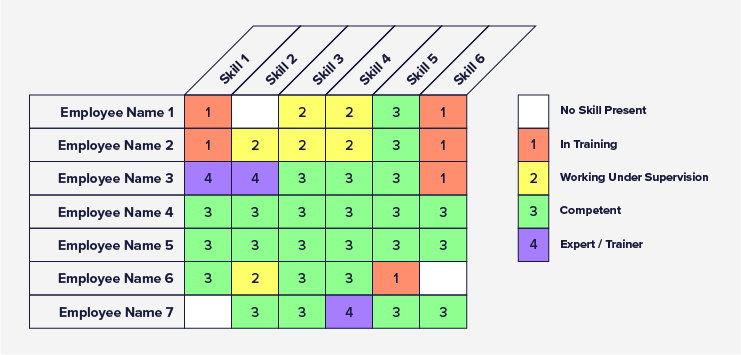
A skills matrix, also known as a competency matrix or training matrix, is a visual reporting tool used for skills tracking and evaluating employee competency across a team or organisation. The matrix typically takes the form of a table, often created in a tool like MS Excel, where usually:
• Row titles contain employee names / titles.
• Column headers show skills, competencies, or qualifications titles.
• With cells indicating the level of competence or capability an individual has. This is usually illustrated as a scale/level of proficiency.
The purpose of the skills matrix is to give an overview of the skills and associated competence of an individual / or team of individuals. The visual nature of the skills matrix report should make the identification of employee gaps (Competence and non-competence) quick and easy.
Why is a Skills Matrix Important? What are the Benefits?
A skills matrix is an essential part of effective workforce development. It enables better skills gap analysis, helps with succession planning, and supports compliance training by making it easier to visualise workforce capabilities. They can be useful to your organisation in multiple ways:
- Identifying Skill Gaps: Visually identify where employees may not be meeting standards or require further training to become competent. This is particularly useful for organisations that have compliance requirements or are required to demonstrate workforce capability, such as those aligning with ISO 9001 quality management standards or ISO 27001 for information security.
- Delivering Training and Development: A skills matrix (or training matrix) helps to target the areas where employee training may be needed most, this aids in ensuring resources are allocated as efficiently as possible to close gaps in competence.
- Succession Planning: The skills matrix can also be used as an indication of who to promote. However, bear in mind, your most technically skilled person may not also be your best leader. Increased and consistent visibility supports Succession Planning and long-term workforce development, by more easily aligning team capabilities with future role requirements.
- Project Management: Identification of employees with the right capability and skills suited to undertaking projects or specific tasks.
- Performance Management: By ensuring the matrix is regularly and accurately updated (which is no easy task!), organisations will be able to track the development of employees’ overtime. This can be useful information to have to hand when conducting performance appraisals and development discussions.
Example uses of a Skills Matrix
- Project Teams Leaders: A skills matrix can assist Project Managers / Team leaders make informed decisions when selecting colleagues to form project teams. The visual nature of the skills matrix makes finding team members that have the right skills and capabilities to work on the project quick and easy.
- HR and Learning & Development: The matrix can be used to quickly identify gaps as well as levels of capability, meaning training programs can be designed to target any specific gaps or weaknesses.
- Talent Management: Using the matrix to identify high performing employees who may be suitable to deliver training to others, help to support long-term workforce development goals or, if they have right potential for promotion to more senior roles.
- Compliance / Quality: In industries with stringent compliance requirements — such as those subject to UK government workforce standards or ISO frameworks — a skills matrix is a powerful way to demonstrate workforce competence. This approach can help to ensure audit preparedness and reduce the risk of non-conformities.
5 Tips for an Effective Skills Matrix
- Keep it Updated and Accurate: The effectiveness of a skills matrix is determined by how accurately it reflects the current capabilities of the workforce. Ensure the skills matrix is tightly controlled and regularly updated to capture any changes in employee skills / competencies.
- Robust Assessments: Assessment of capability and skills should be robust and able to deliver data that, when added to skills matrix, gives an accurate reflection of the employees’ skill level. If appropriate, engage with employees directly as part of the assessment process. This can help promotes ownership of their development as well as in some cases, deliver a more accurate representation of capability.
- Focused and Goal Driven: The information captured by the skills matrix should aim to align with overall strategic objectives of the organisation. As a considerable amount of diligence is required to manually maintain the skills matrix, ensuring that only relevant information helps to drive forward the goals of the organisation should be captured. For example, only capturing the data for skills where there is a compliance requirement.
- Present Data Visually: Use of colour within the matrix will help to highlight areas of strength and weakness, and in turn make the matrix more intuitive and easier to interpret.
- Use Technology: As mentioned earlier, keeping a skills matrix up-to-date and accurate manually tends be not only time-consuming, but suspectable to errors. Left unchecked, these errors could have a negative impact on goals of the organisation (E.g. failed compliance audit, wrongly allocating employees to tasks). Leveraging a dedicated Skills Matrix and Competency Management System, such as SkillStation, will greatly reduce the workload of this process and will reduce the risk of error considerably. As SkillStation is designed to give you the tools to conduct data collection, assessment, and reporting, it makes it much easier to maintain accuracy and utilise the full value of your skills matrix. This technology driven approach will allow you to slice and dice employee data in several different ways very quickly, providing you with insights that may not have been possible with a static, manually maintained skills matrix.
Conclusion
A skills matrix, if kept to an extremely high standard of accuracy, can be invaluable tool for organisations to track and improve the skills and capability of their workforce. When utilised correctly, the benefits of a skills matrix are.
- Give the complete picture of employee competency and capability, allowing skills gaps to be closed effectively.
- Optimise and inform organisational decision-making, from project team composition to planning training initiatives.
- Supporting career development and succession planning by highlighting the areas of required development and focus.
Whether you’re a manager, HR professional, or team leader, utilising a skills matrix / training matrix will help you better understand the composition of your workforces’ strengths and areas for development.
Ready to simplify your skills matrix process? Explore SkillStation — the complete solution for managing training, skills, and competence across your workforce.